Install OpenShift Local and OpenShift Dev Spaces
-
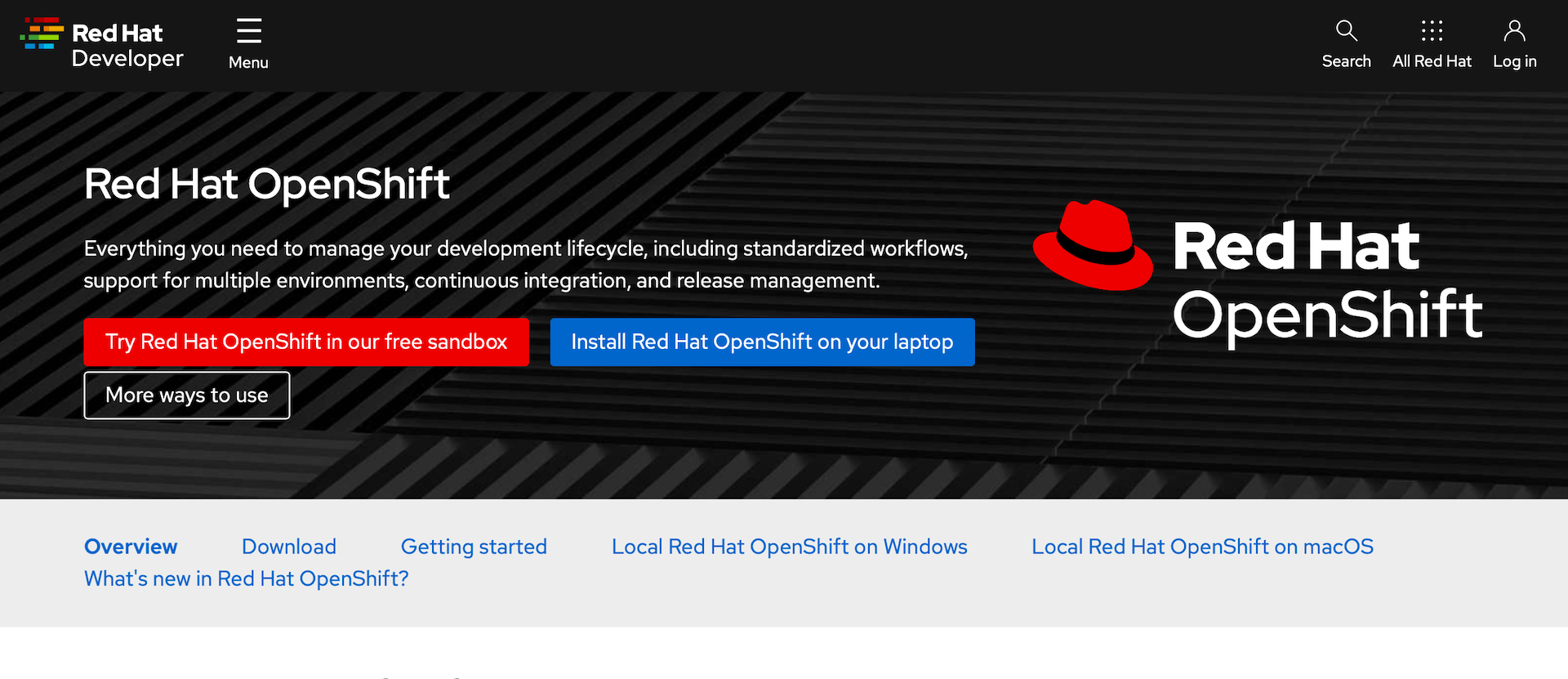
Go To: https://developers.redhat.com/products/openshift/overview
-
Select
Install Red Hat OpenShift on your laptopThis will take you to a login page. If you don’t have a Red Hat developer account you will register for one here. It’s free and you’ll get access to a lot of ebooks, guides, and tools.
-
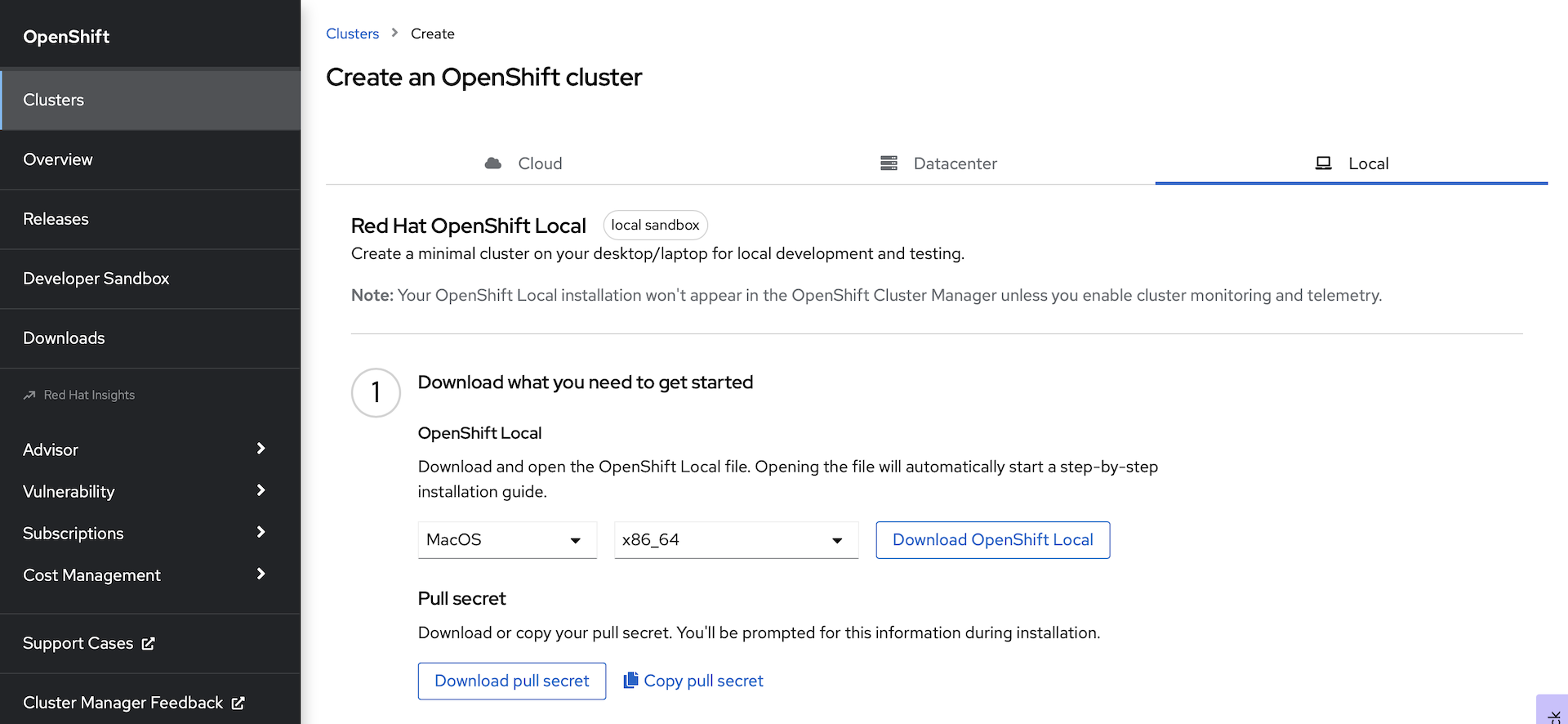
From the landing page after you log in, you will need to download two things:
-
Download the OpenShift Local installation package for your OS and architecture
-
Download your pull secret. This will give you access to all of the Operators in the Red Hat operator catalog.
-
-
Install OpenShift Local with the installation package that you downloaded.
-
Open a terminal and prepare your workstation to run the cluster:
crc setupNote: This will take a while. OpenShift Local will first download the latest cluster bundle, decompress it, and set up your system to run the cluster.
-
Configure your OpenShift Local cluster: Note: You need at least 16GB of RAM on your workstation, 32GB is better.
Adjust the settings below based on your workstation config.
If you only have 16GB of RAM, change memory 16384 to memory 12288.
If you only have 2 CPU cores, (4 threads), then change cpus 6 to cpus 4
crc config set cpus 6
crc config set memory 12288
crc config set disk-size 100
crc config set kubeadmin-password crc-admin
-
Start OpenShift Local:
crc startAfter the cluster starts, you should see output similar to:
INFO All operators are available. Ensuring stability... INFO Operators are stable (2/3)... INFO Operators are stable (3/3)... INFO Adding crc-admin and crc-developer contexts to kubeconfig... Started the OpenShift cluster. The server is accessible via web console at: https://console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing Log in as administrator: Username: kubeadmin Password: crc-admin Log in as user: Username: developer Password: developer Use the 'oc' command line interface: $ eval $(crc oc-env) $ oc login -u developer https://api.crc.testing:6443
Install the OpenShift Dev Spaces Operator
-
Launch the OpenShift console in your browser:
crc console -
Log in with user:
kubeadmin, password:crc-admin -
Navigate to the
Operator Hub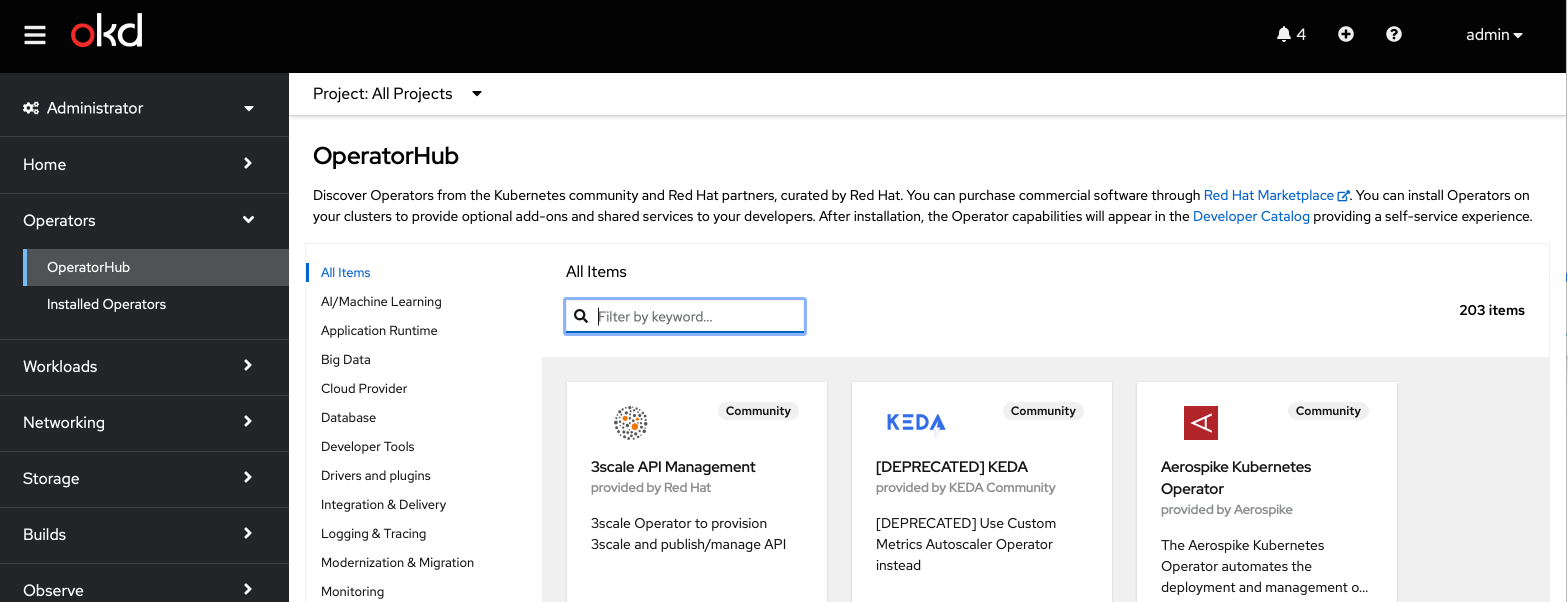
-
Type
dev spacesinto the search, and selectRed Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces: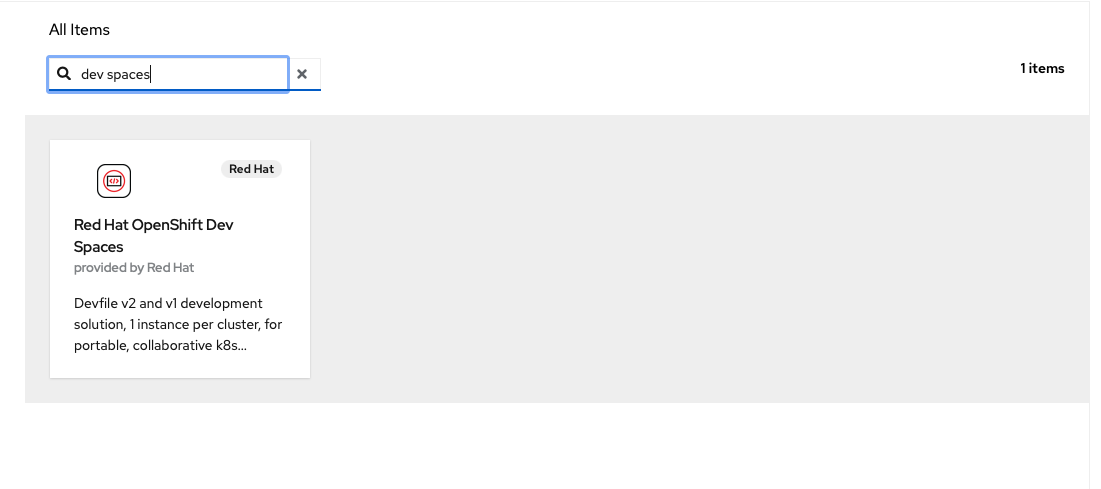
-
Click
Install:
-
Click
Install: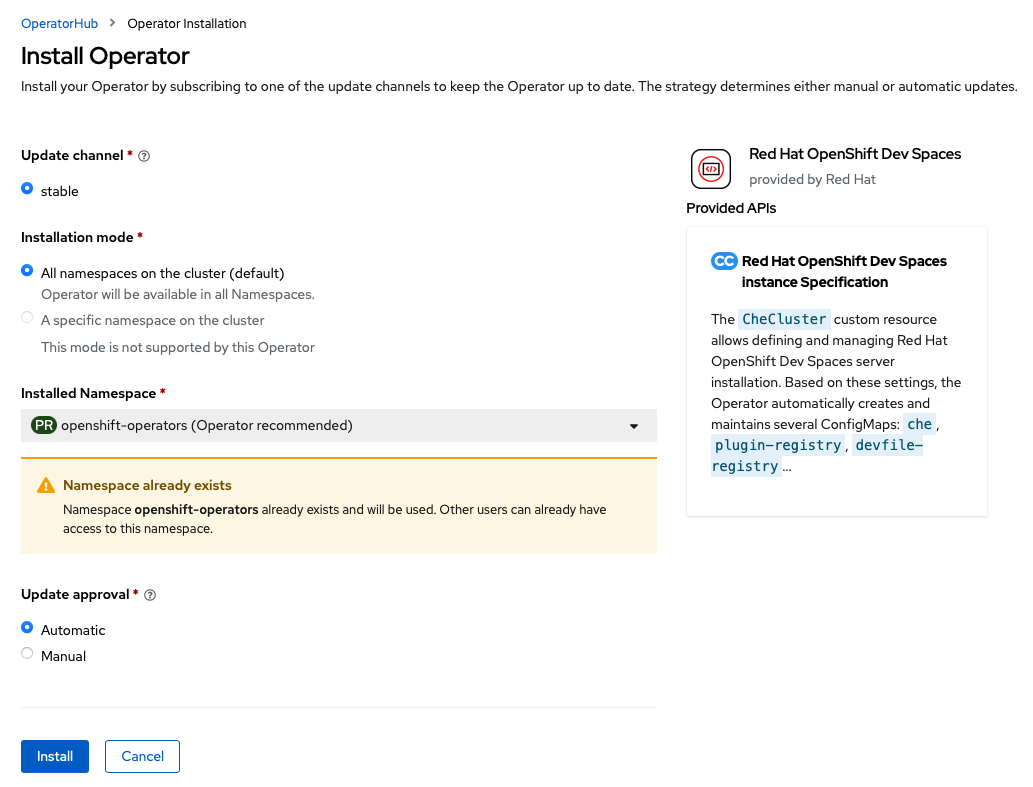
The Operator should begin installing:
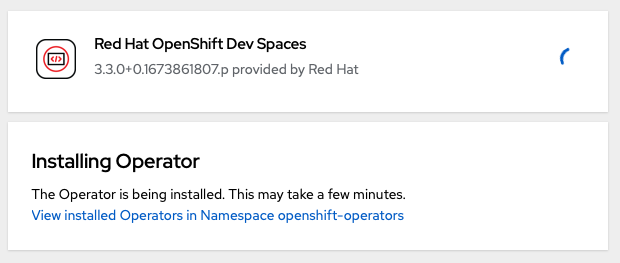
-
Observe the installed Operators, by clicking on
Installed OperatorsunderneathOperator Hubin the left nav menu bar: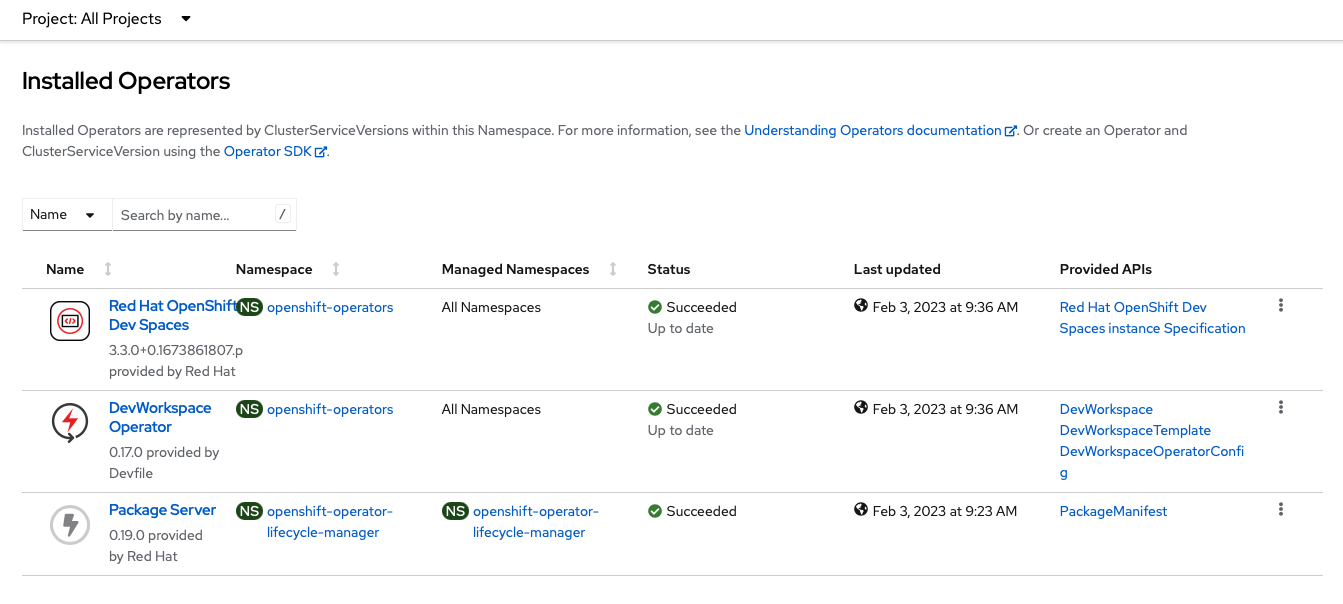
Create the OpenShift Dev Spaces CheCluster Instance
-
Open a terminal and login to the OpenShift Local instance with the CLI:
oc login -u kubeadmin -p crc-admin https://api.crc.testing:6443cat << EOF | oc apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: openshift-devspaces --- apiVersion: org.eclipse.che/v2 kind: CheCluster metadata: name: devspaces namespace: openshift-devspaces spec: components: cheServer: debug: false logLevel: INFO metrics: enable: true pluginRegistry: openVSXURL: https://open-vsx.org containerRegistry: {} devEnvironments: startTimeoutSeconds: 300 secondsOfRunBeforeIdling: -1 maxNumberOfWorkspacesPerUser: -1 maxNumberOfRunningWorkspacesPerUser: 5 containerBuildConfiguration: openShiftSecurityContextConstraint: container-build disableContainerBuildCapabilities: false defaultEditor: che-incubator/che-code/latest defaultNamespace: autoProvision: true template: <username>-devspaces secondsOfInactivityBeforeIdling: 1800 storage: pvcStrategy: per-workspace gitServices: {} networking: {} EOF -
Wait for the Dev Spaces cluster to complete its rollout:
In the console, select from the left hand nav menu
Workloads -> Pods, Then select theProject:openshift-devspacesfrom the drop down in the top left.When the rollout is complete, the list of running pods should look somethings like:
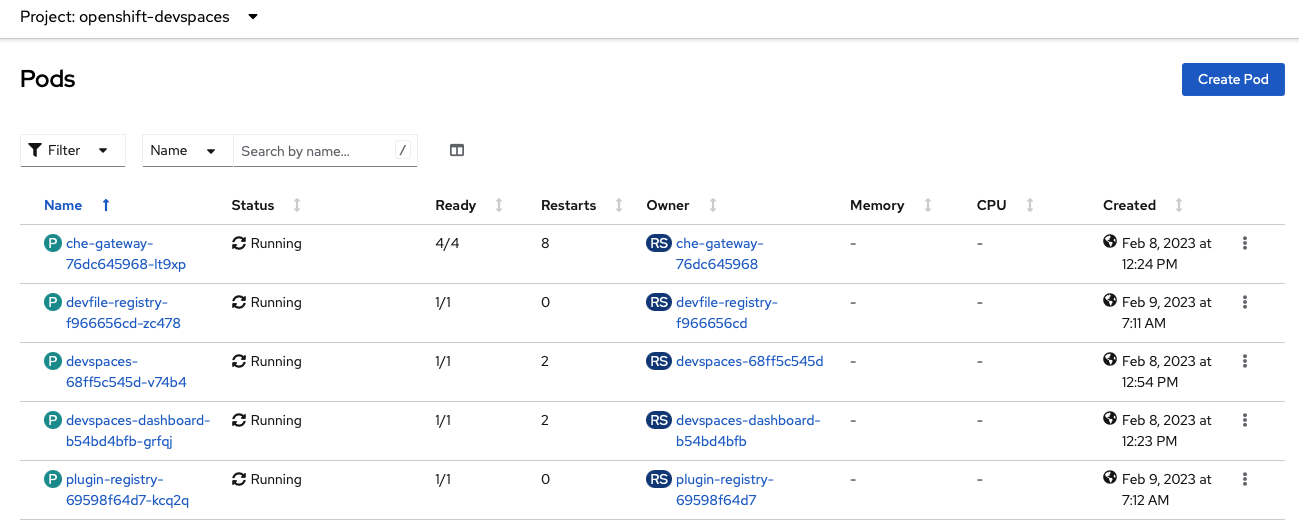
You can now proceed with creating a Dev Spaces Workspace.